拒绝重复发明轮子,向大师们致敬
7 月 18 号,开讲
主要议程
- Java API 扩展
- 配置管理
- Web 特性
Java API 扩展
主要是 java 5 ~ Java 9
语言相关
java.lang 以及扩展
String 为什么 final , private final byte[] value; 为什么要 final ,
主要是因为它不想被继承被覆盖。继承可以覆盖,会有多态行为。会产生一些不确定因素,String 的不变性就会发生改变。
java.lang.CharSequence @since 1.4
字符串通常会有长度的
字符串长度
- 场景
- 非空
- 完全空字符串
- 空格、换行
- 空
- 长度判断
- 非空
- 框架
- Apache Commons lang (目前已经 3.x)
- 2.x
org.apache.commons.lang
- 3.x
org.apache.commons.lang3
- 2.x
- Apache Commons lang (目前已经 3.x)
不同的方法,避免类冲突。
String
#subString
charSequence
-
#subSequence更底层 -
#toString返回String
org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils
#isNumeric
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("as", "sdf", "12", "34", "23", "", null)
.filter(Objects::isNull) // 方法是从 JAVA 8 开始的, Objects 是从 Java 7 开始的
.filter(StringUtils::isNoneBlank) // apache Commons langs
.filter(StringUtils::isNumeric)
.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.of("as", "sdf", "12", "34", "23", "", null)
.filter(org.springframework.util.StringUtils::hasText) // Spring framework
.filter(StringUtils::isNumeric)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
集合相关
- 场景
- 非空
- 空
- 大小判断
注释写在上边是业务场景,写在后边是补充注释。
Spring 也有很多东西不符合国际公约
国际规约不允许以
I开头为接口, 但是 Thymeleaf Eclipse 很多软件都是的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
package com.darian.util;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.MapSerializer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.EnumSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = List.of("2", "3", "4");// since 9
// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
//stringList.add("4"); // ImmutableCollections 不变的
System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(stringList)); // apache Commons Collections
System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isFull(stringList)); // apache
System.out.println(org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(stringList)); // Spring framework
Map<String, String> maps = Map.of("A","A","c","c");
System.out.println(org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(maps));
// 使用场景有关系
// Spring Framework < Apache commons lang(<=4 的时候依赖)
// Spring Framework <5 => Apache commons logging(不再需要了)
// Spring Frameowrk >=5 -> Spring JCL
// Apache Commons Lang 2.4 & 2.6 会有一些不兼容
}
{
// Effective Java II 都是不变的对象
EnumSet<TimeUnit> timeUnits =
EnumSet.of(TimeUnit.DAYS, TimeUnit.HOURS);
}
}
使用场景有关系
- Spring Framework < Apache commons lang(<=4 的时候依赖)
- Spring Framework <5 => Apache commons logging(不再需要了)
- Spring Frameowrk >=5 -> Spring JCL
- Apache Commons Lang 2.4 & 2.6 会有一些不兼容
I/O相关
org.springframework.util.StreamUtils
org.springframework.util.StreamUtils#copyToString
配置管理
Java 系统属性
java.lang.System#getProperty(java.lang.String)
java.lang.System#getProperties
Java 程序参数
-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
等价于 System.setProperty("file.encoding","UTF-8")
参数解析
Spring Boot 启动参数: --server.port=9090
Spring :
org.springframework.core.env.SimpleCommandLineArgsParser
Spring @TestPropertySource#properties
@TestPropertySource#locations
同一个 @TestPropertySource 有两个不同的优先级。
Java 配置文件
Environment 也是 Spring 中的,
就是重复发明轮子,
Apache commons configuration
- JNDI
- JDBC Datasource
- System properties
- ……
在 Spring Boot 里边都有
自古文人都是贼,相互的抄袭
Spring Demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;
@SpringJUnitConfig
@TestPropertySource(properties = {"name = darian", "age=32"})
public class SpringPropertyTest {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("name:" + environment.getProperty("name"));
System.out.println("age:" + environment.getProperty("age",Integer.class));
}
}
apache
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class ConfigPropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ConfigurationException {
URL resourceURL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()
.getResource("application.properties");
Configuration configuration = new PropertiesConfiguration(resourceURL);
System.out.println(configuration.getInt("age"));
}
}
org.apache.commons.configuration.PropertyConverter
org.springframework.beans.SimpleTypeConverter
org.springframework.beans.TypeConverterSupport
org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter#convertIfNecessary(java.lang.Object, java.lang.Class<T>)
org.springframework.beans.TypeConverterSupport#doConvertorg.springframework.core.convert.support.DefaultConversionService
org.springframework.core.convert.support.StringToNumberConverterFactory.StringToNumber#convert
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private static final class StringToNumber<T extends Number> implements Converter<String, T> {
private final Class<T> targetType;
public StringToNumber(Class<T> targetType) {
this.targetType = targetType;
}
// 这个方法是转化类型的。
public T convert(String source) {
return source.isEmpty() ? null : NumberUtils.parseNumber(source, this.targetType);
}
}
apache 1.1 2005
spring 3.0 2009 年
Apache Commons Configuration since 1.1 Propertycoverter
Spring framework since 3.0 Converter
Spring 重复发明轮子是一等的成功。
Web 特性
模板引擎
Turbine 涡轮。
Spring Cloud hystrix 里边有 搜集的功能。
Apache Turbine™ Web Application Framework
Apache Turbine™ is a servlet based framework that allows experienced Java developers to quickly build web applications. Turbine allows you to use personalize the web sites and to use user logins to restrict access to parts of your application.
Turbine is a matured and well established framework that is used as the base of many other projects (like e.g. the excellent Jetspeed 1 Portals framework.
Turbine is an excellent choice for developing applications that make use of a services-oriented architecture. Some of the functionality provided with Turbine includes a security management system (decoupled in Fulcrum Security), a scheduling service, XML-defined form validation server (Fulcrum Intake), and an XML-RPC service for web services. It is a simple task to create new services particular to your application.
The Turbine core is free of any dependency on a presentation layer technology. Both JavaServer Pages (JSP) and Velocity are supported inside Turbine. For developers already familiar with JSP, or have existing JSP tag libraries, Turbine offers support for the Sun standard. Velocity is the favorite view technology of most users of the Turbine framework; try it out and see if Velocity can help you develop your web applications faster and work more easily with non-programming designers.
Turbine is developed in an open, participatory environment and released under the Apache Software License. Turbine is intended to be a collaboration of the best-of-breed developers from around the world. We invite you to participate in this open development project. To learn more about getting involved, look at our “How to Help” pages.
SOA
Turbine: JSP + velocity 混用
Spring webMVC
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver
- JSP
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
- velocity
VelocityViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver
1
2
3
4
// 把多个 viewResolver 放到一起。
public void setViewResolvers(List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers) {
this.viewResolvers = viewResolvers;
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#render 渲染方法
Spring 从创意上就是抄袭的。
REST 支持
Spring Web MVC / WebFlux
- Annotation :
@Controller、@RequestMapping - 请求映射
@RequestMapping、@GetMapping producers、consumers
JAX-RS ( Java REST )
@GET、@POST、@PUT、@DELETE、@HEAD@Produces、@Consumes
JAX-RS 规范,
内容协商
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Content_negotiation
rest 协议 有一个 自描述消息。 406 (Not Acceptable)
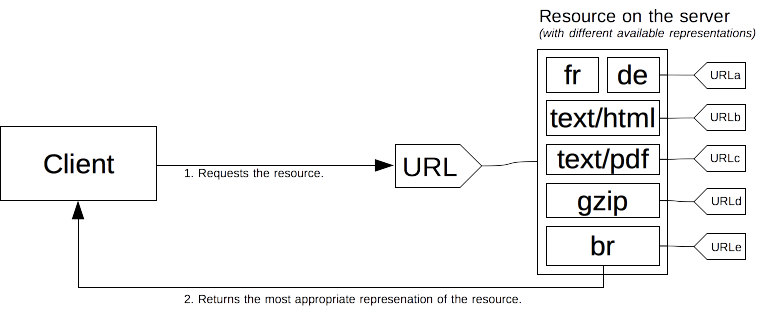
Principles of content negotiationSection
A specific document is called a resource. When a client wants to obtain it, it requests it using its URL. The server uses this URL to choose one of the variants it provides – each variant being called a representation – and returns this specific representation to the client. The overall resource, as well as each of the representations, have a specific URL. How a specific representation is chosen when the resource is called is determined by content negotiation and there are several ways of negotiating between the client and the server.
The determination of the best suited representation is made through one of two mechanisms:
- Specific HTTP headers by the client (server-driven negotiation or proactive negotiation), which is the standard way of negotiating a specific kind of resource.
- The
300(Multiple Choices) or406(Not Acceptable) HTTP response codes by the server (agent-driven negotiation or reactive negotiation), that are used as fallback mechanisms.Over the years, other content negotiation proposals, like transparent content negotiation and the
Alternatesheader, have been proposed. They failed to get traction and got abandoned.
save
org.springframework.web.accept.HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy
客户端请求服务端的时候,请求头里边有 Accept: 告诉服务器,我可以接受你什么格式。
服务器根据你的内容,做一个预判。
根据 consumes 请求到不同的方法上边去。
Web 异步化
Web Reactive
自动装配
spring 4.x -> spring boot 1.x
spring 5.x -> spring boot 2.x
你要不要重复的发明轮子去做。