议题
- Servlet 介绍
- Servlet 组件
- Spring 运用
Spring、高并发、
重要的是规范
Servlet 8 大组件,我们在开发的过程中很少用到 Servlet 的组件,现在都是 Spring MVC,SSM 。
Servlet 介绍
Servlet
Servlet 是一种基于 Java 技术的 Web 组件,用于生成动态内容,由容器管理。类似于其他 Java 技术组件,Servlet 是平台无关的 Java 类组成,并且由 Java Web 服务器加载执行。通常情况,由 Servlet 容器提供运行时环境。Servlet 容器,有时候也称作为 Servlet 引擎,作为Web服务器或应用服务器的一部分。通过请求和响应对话,提供Web 客户端与 Servlets 交互的能力。容器管理Servlets实例以及它们的生命周期。
从功能上,Servlet 介于 CGI(Common Gateway Interface)与服务扩展(如:Netscape Server API 或 Apache 模块)之间。
在体系上,Servlet 技术(或者规范)属于 Java EE 技术(规范)的一部分。不过 Servlet 并非一开始就隶属于 J2EE 或者 Java EE。接下来的小节将会介绍 Servlet 各个版本。
Servlet 组件
组件:
Servlet
Filter
Listener
Spring 运用

Spring 运用
Servlet 运用
Filter 运用
Listener 运用
Servlet 介绍
HTTP
- payLoad
- body
- header
访问的时候,并不是访问的域名,而是访问的是DNS解析出来的远程地址。
https
Remote Address : DNS 解析的远程地址。
Nginx 接收信息,转发,到后端的处理器去进行处理,对应的信息会去解析。
Request 是输入,
www 是万维网的约定,不是协议 。HTTP 是 协议,ftp是协议。
Servlet 是一个规范,我有一个API 有一个相应的编程的模式,约定了我相应的一个走向,webFlux。
jquery - bootstrap - angurajs - reator 这是前端的一个编程模型的发展
API 是共用的,我和大家都共用API,至于你用什么样的容器,我就不管了,Spring Boot 都有很多种容器,Tomcat 是 Servlet 容器,jetty、undertown 都是 Servlet 容器。
对于我编程人员来说,不需要了解那么多细节,如果丢给你 header,body 全部丢给你,那么瞬间就懵逼了,
accept : 自描述消息,我这个客户端可以接收哪些消息,html.xml, q = 0.9 这叫 匹配因子,这里有容器相应的处理,然后返回去
http 是文本协议,需要相应的视图去渲染,所以需要不同的格式,由不同的渲染逻辑去渲染。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_servlet
Servlet API version Released Specification Platform Important Changes Servlet 4.0 Sep 2017 JSR 369 Java EE 8 HTTP/2 Servlet 3.1 May 2013 JSR 340 Java EE 7 Non-blocking I/O, HTTP protocol upgrade mechanism (WebSocket)[14] Servlet 3.0 December 2009 JSR 315 Java EE 6, Java SE 6 Pluggability, Ease of development, Async Servlet, Security, File Uploading Servlet 2.5 September 2005 JSR 154 Java EE 5, Java SE 5 Requires Java SE 5, supports annotation Servlet 2.4 November 2003 JSR 154 J2EE 1.4, J2SE 1.3 web.xml uses XML Schema Servlet 2.3 August 2001 JSR 53 J2EE 1.3, J2SE 1.2 Addition of FilterServlet 2.2 August 1999 JSR 902, JSR 903 J2EE 1.2, J2SE 1.2 Becomes part of J2EE, introduced independent web applications in .war files Servlet 2.1 November 1998 2.1a Unspecified First official specification, added RequestDispatcher,ServletContextServlet 2.0 December 1997 N/A JDK 1.1 Part of April 1998 Java Servlet Development Kit 2.0[15] Servlet 1.0 December 1996 N/A Part of June 1997 Java Servlet Development Kit (JSDK) 1.0[9]
2.3 filter。Servlet 有一个事件监听的支持, EventListener
3.0 以后,支持可插拔的方式,动态的部署。
3.0 只是一个 编程方式的提升,还有易于部署,还有内置的web。
Security : 安全,
Spring Cloud Security 跟 Java Security 还有 servlet security 相比真的是小儿科。
小巫见大巫。
Spring security 、servlet security 都很难用。
3.1 实现了非阻塞 IO,
tomcat 里边实现是有 NIO 的是西安的,
HTTP protocol upgrade mechanism 是 http 协议,是 http 握手的时候,直接进行升级,直接从 http 编程 socket ,必须由高端的浏览器去支持。
web Reactive
Servlet 3.1 did provide an API for non-blocking I/O.
异步 + 非阻塞,就是 Reactive ,主要是 webStream 的规范,主要是通过 webFlux 一套统一的 API ,实现统一的编程模型。所谓的 流式的计算,
P1, p2, p3 一个一个的计算,具有相应的过程,核心就是不关注你的是否异步的过程。
lombda 语法。
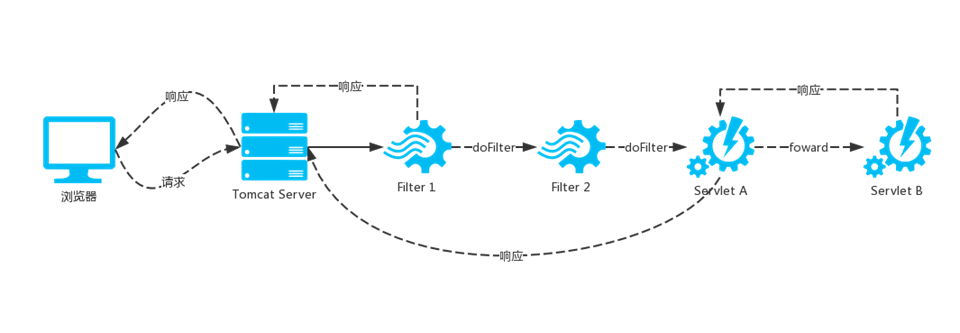
- 浏览器
- tomcat Servet
- filter
- servlet
“ISO-8859-1” 是默认的编码,中文乱码,就搞个 filter
filter 哪个先,哪个后,怎么搞?了解你里边发生的事情,换一种技术能不能解决才是关键。Servlet 规范,
Java™ Servlet Specification Version 2.4
SRV.6.1.1 Examples of Filtering Components • Authentication filters (认证) • Logging and auditing filters (日志) • Image conversion filters (图片转换) • Data compression filters (数据压缩) • Encryption filters (加密) • Tokenizing filters (Token) • Filters that trigger resource access events • XSL/T filters that transform XML content • MIME-type chain filters • Caching filters
token 是一个 GWT 所谓的 token 的令牌,Spring security
网关怎么做 ?zuul 一个场景不应该和一个技术画一个等号,问题是不用 servlet ,也是可以
Filter Lifecycle 生命周期。
Servlet 组件
JSP 九大内置对象
- Application ServletContext
- session httpSession
- request httpServlet request
- page jspServletContext
- out
微博,你用 jsp 可以实现,themplief 也可以,工作效率,性能的问题,团队的问题,
大家都不会 JSP,你就不要搞 JSP ,
Application Lefecycle Events 生命周期
JSP 是你所有你能看到的视图渲染的性能最好的框架。
它是编译的时框架,
运行时解释,编译时解释有区别,
第一次请求很慢,你可以去解决。不是问题。
javax.servlet.ServletRequestListener ServletRequestAttributeListener
Java 那么多源码,没有重点,没有分析,抓不着头脑,
了解原理之后,就不需要看那么多的源码,
你创作一首诗,不见得把《唐诗三百首》全部都背下来,你看着看着,这本书,哇偶,这本书看不下去了。
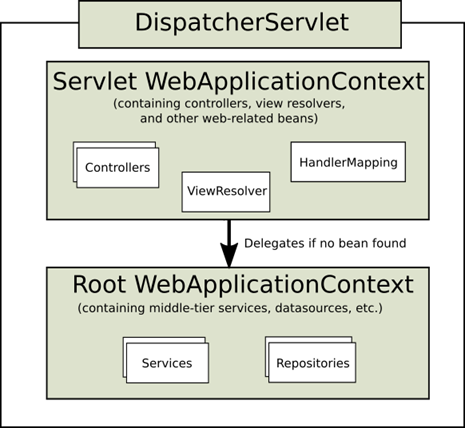
DispatcherServlet 为什么叫 DispatcherServlet
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/
1.0.0 api/
2004-03-23 06:00
叫做前端总控制器。
J2EE pattern http://www.corej2eepatterns.com/
Servlet WebApplicationContext
Root webApplicationContext
Root WebApplicatoin 读不到 Servlet WebApplicationContext 里边的东西,
Serlvet context -> servletContextListener
javax.servlet.ServletContextListener
1
2
3
4
5
6
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
// 上下文初始化
void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent var1);
// 销毁
void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent var1);
}
javax.servlet.ServletContextListener 实现:
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerorg.springframework.web.context.ContextCleanupListenerorg.springframework.web.util.IntrospectorCleanupListenerorg.springframework.web.util.WebAppRootListener
我在应用启动的时候就启动了
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
1
2
3
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
} else {
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
ApplicationContext parent = this.loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
} else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" + WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
} catch (RuntimeException var8) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", var8);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var8);
throw var8;
} catch (Error var9) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", var9);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, var9);
throw var9;
}
}
}
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
1
2
3
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
只允许你有一个 Root-we application ,如果启动的时候发现你有了,就会启动失败了,不能启动了
1
2
3
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = this.createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
如果为空,创建一个应用的上下文,
看源码要,观其大意。
1
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
创建好以后,存进去,
你定义两个 Listener 以后,启动的时候,就会报错。
其它东西,不要看,枝末细节,是在调试的时候,再去看,问题出现在哪个地方,调试地方。
代码要看版本。
public 方法一般不会大改。
java.lang.ClassLoader
1
2
3
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parent) {
this(checkCreateClassLoader(), null, parent);
}
默认的构造,里边,传一个parent 过来,
双亲委派,
链表,
看你前一个链,看看加载进来了没有,再看自己加载了没有。
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
public AbstractApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
this();
this.setParent(parent);
}
也会有一个父的 parent
我可以没有 双亲。
Root_web 先启动,Servlet 再启动,分析一下。
SRV.2.3 Servlet Life Cycle A servlet is managed through a well defined life cycle that defines how it is loaded and instantiated, is initialized, handles requests from clients, and is taken out of service. This life cycle is expressed in the API by the init, service, and destroy methods of the javax.servlet.Servlet interface that all servlets must implement directly or indirectly through the GenericServlet or HttpServlet abstract classes.
初始化完成,不代表启动完成,
启动完成代表所有的组件都已经加载完毕。
ContextConfigLocation
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
5
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
//。。。
configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation");
//。。。
}
创建的时候,通过上下文的配置读进来,上下文创建的时候加以配置。
先创建好,但是没启动,启动的时候,再去读这个东西,
ContextConfigLocation 是给 ContextLoaderListener 用的。
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
什么时候初始化,
Loading 是加载的意思,Instantiation 是实例化,实例化不等于初始化,实例化是 new 的意思。初始化时 Initializa 调用
javax.servlet.Servlet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public interface Servlet {
// 初始化,配置 contextConfigLoacation
void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException;
ServletConfig getServletConfig();
void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException;
String getServletInfo();
void destroy();
}
javax.servlet.ServletConfig
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public interface ServletConfig {
String getServletName();
ServletContext getServletContext();
String getInitParameter(String var1);
Enumeration getInitParameterNames();
}
javax.servlet.GenericServlet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
public void init() throws ServletException {
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
}
PropertyValues pvs = new HttpServletBean.ServletConfigPropertyValues(this.getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// webxml 配置项和字段进行了一个绑定
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(this.getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, this.getEnvironment()));
this.initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (BeansException var4) {
if (this.logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
this.logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'", var4);
}
throw var4;
}
}
this.initServletBean();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
HttpServlet
HttpServletBeanFrameworkServletDispatcherServlet
通过 内省 将字段和我的配置项绑定起来。
1
2
3
4
<init-param>
<param-name>namespace</param-name>
<param-value>darian</param-value>
</init-param>
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#init 是final 方法,如果子类想要扩展中间有
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#initServletBean 允许你的子类,通过 initSerlvetBean 去进行扩展,
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initServletBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
this.getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext();
this.initFrameworkServlet();
} catch (ServletException var5) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var5);
throw var5;
} catch (RuntimeException var6) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", var6);
throw var6;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + this.getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
ContextLoader 必然再 FrameworkServlet 之前。
ContextLoderListener 会把我的 ROOT 加载好,同时,这个 ROOT 会做我的 DispatcherServlet。
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(this.getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
this.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = this.findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = this.createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
this.onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = this.getServletContextAttributeName();
this.getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + this.getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
ContextLoader 里,加载了 WebApplicationContext 的 ROOT 上下文。上下文的东西就是同一个
rootContext 不一定有,web.xml 中没有定义的时候,就没有。
1
2
3
4
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 等于空,我去find,不一定要自己去创建。
// 创建的时候,把 Servlet上下文 的 parent 提交给了 ROOT
Spring 是利用了 Servlet 的一些机制来完成他的操作。
n -> y 是否阻塞。
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=*:5005
调试发现 Root WebApplicationContext 被 Servlet WebApplicationContext 加载作为父parent
Servlet 启动,调用的是默认的构造器,当 wac 为空的时候,会去取上下文里边的属性,关联的上下文找不到的时候,就会去创建它,
Spring 就是利用 Servlet 的这套机制。非常的了解 J2EE 的机制。
Filter
javax.servlet.Filter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public interface Filter {
void init(FilterConfig var1) throws ServletException;
void doFilter(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2, FilterChain var3) throws IOException, ServletException;
void destroy();
}
org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter字符编码的 filterorg.springframework.web.filter.CompositeFilter合并org.springframework.web.filter.CorsFilter跨域org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxySpring security 理由
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<!-- 我这个 filter 只为我的 DispatcherServlet 服务 -->
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
</filter-mapping>
filter 不管你怎么样,执行完以后,才执行 DispatcherServlet 的 doService
filter 先定义先执行。
URL pattern 的匹配规则。
匹配度高的先执行