为什么学习源码?
- 工作
- 面试
本期议题
- 为什么学习源码
- 怎么样学习源码
- 如何运用源码
小马哥新书:
《Spring Boot 编程思想》
- 系统学习,拒绝浅尝辄止
- 重视规范,了解发展趋势
- 场景分析,掌握技术选型
- 源码解读,理解设计思想
- 实战演练,巩固学习成果
为什么要学习源码
- 挑战高薪
- 不是当将军的士兵不是好士兵,环境所逼而已
- 架构设计
- 个人成长
- 兴趣爱好
- 要看你个人的兴趣
- 排查问题
前三年,外企。英雄不问出处,流氓不问岁数。
同事,西安交大,国防科技大的教授。
外企,考试,考试 JAVA ,后来,考了第一名
学习源码,要多写代码。大学时期就写了很多的代码。
外企很注重规范。JPA 是 10 年前的东西!!! SCJP JPA 规范。07 年。
要学习规范,SCJP SCDP 要考试规范,老外 :“中国没有高级程序员!”
怎样学习源码?
- 限定范围
- 提出问题
- 积累基础
- 猜测实现
- 对比源码
- 学习规范
注重原始的积累。
北宋年间。苏东坡,一本书从头至尾的看,
《惠州一绝》
日尝荔枝三百粒,不辞常作岭南人
类型转化,为什么
Spring做的比较好。猜完以后要对比一下。
要把所有的代码都写出来,一种业务,多种实现,
学习源码只是一种实现。
JMX
都有消息确认
- activemq
- kafka
- RocketMq
AMQP
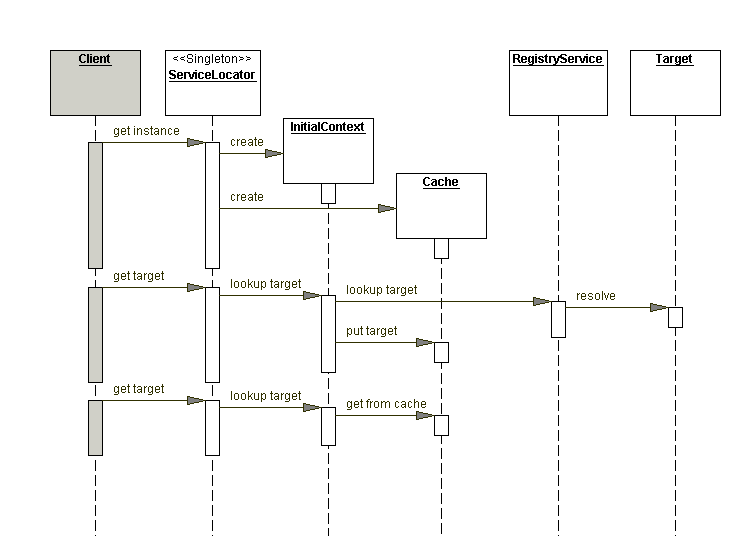
Spring IOC
1. The IoC Container
This chapter covers Spring’s Inversion of Control (IoC) container.
1.1. Introduction to the Spring IoC Container and Beans
This chapter covers the Spring Framework implementation of the Inversion of Control (IoC) principle. (See Inversion of Control.) IoC is also known as dependency injection (DI). It is a process whereby objects define their dependencies (that is, the other objects they work with) only through constructor arguments, arguments to a factory method, or properties that are set on the object instance after it is constructed or returned from a factory method. The container then injects those dependencies when it creates the bean. This process is fundamentally the inverse (hence the name, Inversion of Control) of the bean itself controlling the instantiation or location of its dependencies by using direct construction of classes or a mechanism such as the Service Locator pattern.
java Beans = POJO / setter / getter / is
- 充血模型 = POJO + 行为操作
-
贫血模型 = POJO
- 富模型
- 瘦模型
java.beans.PropertyDescriptor
Bean 的内省,用来做 Bean 。
方法签名是和 JVM 一样的。
JVM 是按照方法签名来加载方法的。
java.beans.Beans#instantiate(java.lang.ClassLoader, java.lang.String)
1
2
3
public static Object instantiate(ClassLoader cls, String beanName) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
return Beans.instantiate(cls, beanName, null, null);
}
java.beans.Introspector
看源码要观其大意,不要看的太细。了解思想。
Object
User
所有的类都继承自 Object ,stopclass ,我阻止它内省了。
1
2
3
4
java.beans.PropertyDescriptor[name=class; values={expert=false; visualUpdate=false; hidden=false; enumerationValues=[Ljava.lang.Object;@3159c4b8; required=false}; propertyType=class java.lang.Class; readMethod=public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()]
java.beans.PropertyDescriptor[name=id; values={expert=false; visualUpdate=false; hidden=false; enumerationValues=[Ljava.lang.Object;@73846619; required=false}; propertyType=class java.lang.Long; readMethod=public java.lang.Long com.darian.studysourcecode.java.beans.User.getId(); writeMethod=public void com.darian.studysourcecode.java.beans.User.setId(java.lang.Long)]
java.beans.PropertyDescriptor[name=name; values={expert=false; visualUpdate=false; hidden=false; enumerationValues=[Ljava.lang.Object;@4bec1f0c; required=false}; propertyType=class java.lang.String; readMethod=public java.lang.String com.darian.studysourcecode.java.beans.User.getName(); writeMethod=public void com.darian.studysourcecode.java.beans.User.setName(java.lang.String)]
bean的内省 不管 java 里边有,Spring 里边也有 ,Tomcat 里边也有。
BeanWrapper 也是利用了 Bean 内省的机制。
JAVA EE
Bean 工厂
lookup
依赖注入
DI = Dependency injection + Dependency lookup
Spring 里边一开始是没有完全的 依赖注入的是实现的。
1
2
@Autowired
private User user;
在它之前也有一个东西。
Java
javax.naming.Context#lookup(javax.naming.Name)
1
2
// 根据 Bean 的名字去查找
public Object lookup(Name name) throws NamingException;
最开始在 Spring 中,是没有
EJB = Local Bean + Remote Bean
- Local Bean : 当前容器
- Remote Bean : 远程 RPC = RMI + Interface = Dubbo 、Spring Cloud
Server 是 Bean
@Server 也是 Bean
Martain flow
Spring 是阉割的 EJB
- Spring Container = Local Bean
- Spring Remote Bean = Spring Cloud = Feign + Service Discovery
了解一个源码,要了解源码。
dubbo 就是 hession 就是 RMI
Tomcat 里边有一个
<Context>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
<GolbalNamingResources>
...
<Resource name="sharedDataSource"
global="sharedDataSource"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
factory="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourceFactory"
alternateUserNameAllowed="true"
username="bar"
passowrd="barpass"
...></Resource>
...
</GolbalNamingResources>
设置共享的数据库。
Spring 里边的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
<bean id="myDataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<!-- results in a setDriverClassName(String) call -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="masterkaoli"/>
</bean>
EJB 写法
1
2
@EJB // 2005 年
private DataSource datasource;
Spring @Autowried // 2007
Annotation 注入
依赖查找 lookup / getBean 都是一样的。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#getBean(java.lang.Class<T>, java.lang.Object...)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object... args) throws BeansException {
Object resolved = this.resolveBean(ResolvableType.forRawClass(requiredType), args, false);
if (resolved == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(requiredType);
} else {
return resolved;
}
}
@Nullable
private <T> T resolveBean(ResolvableType requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean nonUniqueAsNull) {
NamedBeanHolder<T> namedBean = this.resolveNamedBean(requiredType, args, nonUniqueAsNull);
if (namedBean != null) {
return namedBean.getBeanInstance();
} else {
BeanFactory parent = this.getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
return ((DefaultListableBeanFactory)parent).resolveBean(requiredType, args, nonUniqueAsNull);
} else if (parent != null) {
ObjectProvider<T> parentProvider = parent.getBeanProvider(requiredType);
if (args != null) {
return parentProvider.getObject(args);
} else {
return nonUniqueAsNull ? parentProvider.getIfUnique() : parentProvider.getIfAvailable();
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
观其大意,就是先找父类,再找子类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
public class UserSpringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NamingException {
/***
* 没有 DataSource 定义
*/
DefaultListableBeanFactory parentBeanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory1 = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
beanFactory1.setParentBeanFactory(parentBeanFactory);
/***
* Spring
*/
// xml 存一下
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
// 写法 1
BeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
User user1 = (User) beanFactory.getBean("user");
// 写法 2
User user = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
applicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
/***
* 传递相应的参数
*/
beanFactory.getBean("user", 1L, "darian");
/****
* EJB
*/
Context context = new InitialContext();
/***
* JNDI = Java Naming And Directory Interface
* Tomcat 容器
*/
Context context1 = (Context) context.lookup("java/com/");
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) context1.lookup("java/com/datasource");
}
}
1
2
// 256 是一个经验值。
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap(256);
版本意识,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class UserBeanSpringDemo {
// <Bean id="user" class="com......">
// <property id="id" value>
// <pro....
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// 理解 Bean 定义 = BeanDefinition
// XML = BeanDefinition
// Annotation 也是 BeanDefinition AnnotationBeanDefinition 是 2.5 以后的。
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(User.class);
// User Bean 定义
AbstractBeanDefinition userBeanDefinition = builder.getBeanDefinition();
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
// <property name="id" value="1L">
propertyValues.add("id", 1L);
// <property name="name" value="Darian1996 ">
propertyValues.add("name", "Darian1996");
userBeanDefinition.setPropertyValues(propertyValues);
// 注册
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("user", userBeanDefinition);
User user = beanFactory.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition
Bean 的创建的方式,
FactoryBean 通过 Factory 来进行构造。
如果不是 FacotoryBean 的时候
是通过 getObject 方法来进行操作。
- 两种 bean
- bean 直接定义掉了
- FactoryBean 返回
XML 是一段文本,类型的描述,类的名称。
#getBeanName
1
2
3
4
ClassLoader classLoader = null;
Class userClass = classLoader.loadClass("com.darian.studysourcecode.java.beans.User");
Constructor constructor = userClass.getConstructor();
User user2 = (User) constructor.newInstance();
策略模式实例化
- 找构造器
我们一定要了解背景。
BeanFacotry Bean 容器 IOC 的容器。
-
bean 定义
-
Bean 类
-
Bean 实例化策略
-
初始化 (pre 、post)
- Bean 存储
-
-
-
-
lazy-init=”false”
- (启动时)早期初始化
- (需要时)延迟初始化
-
scope
- 单例
- 原生
懒汉式。延时加载要少用。问题要提早暴漏。
要观其大意,多了解基础。
你的同事提供方案时,只给你一个方案,那么他不是一个好的工程师。
你的技术的积累应该来自于自己的学习方法的积累。
舞台能提高你的视野,修行还是看个人。
多写代码,才能融会贯通
技巧:多加几个qq群,微信群,别人的问题,当作自己的问题去理解。
Java 内存模型大家都没有一个标准。哈哈哈,监听则明。
maven
1
2
3
4
<plugins>
<plugin>
</plugin>
</plugins>
- 架构师
- 写代码要靠谱
- 做方案要更靠谱才行