Spring
- JMX 是 JAVA 中很重要的东西。
- 实现需求
- 满足设计
有时候批评中医不是科学,西医是科学
开发
- 功能性需求
- 扩展性,功能变化
- 非功能性需求
- 成本
- 性能
- 管理和控制
收入增加不了,但是对你本身有帮助,
你基础越好,对你未来更有帮助。
- JAVA
- SCJP、SCWCD、SCBCD
JAVA 的专家组还是很牛逼的。JAVA
http 、TCP、reactive 为什么中国人没有,外国人有?
首先要站在巨人的肩膀上,更重要的是还要知道它的整个的发展历程。
议程
- JMX
- JMX 客户端
- Spring Boot 整合
JMX
介绍
JMX 全称 Java Management Extensions,技术提供构建分布式、Web、模块化的工具,以及管理和监控设备和应用的动态解决方案。从 Java 5 开始,JMX API 作为 Java 平台的一部分。
架构
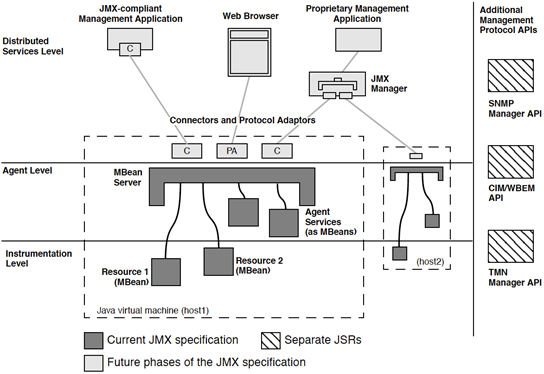
管理Bean(MBeans)
-
标准 MBeans
设计和实现最为简单,Bean的管理 通过接口方法来描述。MXBean 是一种特殊标准MBean,它使用开放MBean的概念,允许通用管理,同时简化编码
-
动态 MBeans
必须实现指定的接口,不过它在运行时能让管理接口发挥最大弹性
JMX
学习 Spring Framework 的话,多多关注一下 JMX。提供 除了本地化,还可以远程话,GPS 可以定位一下 JAVA 本地进程的 ID,但是你要远程要 Jmap 要 dump 一下内存,你就没办法了。你就只能在本地去搞。
设备层、代理、
设备提供 JMX 的一些资源。代理主要做一个 门面 一样的东西,让外边的人去访问。
外边有很多种客户端,你可以有 JAVA 的方式,JAVA 有一个 RMI ,远程方法调用,用 Web 浏览器的方式,你要兼容它的规范,它的协议里边有规定,规定包括客户端和服务端两个部分。因此我们的 Jconsole 或者 jmap 去连接到时候,它会遵守规范,比如说,Contector 和 协议的Adapter (适配器)
管理Bean
jcp.org : JAVA 的规范
《JavaTM Management Extensions (JMXTM) Specification, version 1.4》
是学术一样的东西
1.4 Component Overview
The key components of each architectural level are listed below and discussed in the subsequent sections.
- Instrumentation level
- MBeans (standard, dynamic, open, and model MBeans)
- Notification model
- MBean metadata classes
- Agent level
- MBean server (服务器)
- Agent services ()
元信息 META-INF 包名,JAVA 类,包,字段,反射里的都是元信息,注解也算,元信息就是描述信息的信息。比如说,字段的内省就是元信息。
C/S 架构,服务端好,客户端不好,
未来云服务架构可能是个伪命题,云服务延伸出来就是 C/S 架构,我们由于成本和科技的发展,有可能每个节点都是服务器,你的电脑是服务器,它的电脑也是一个服务器。每个计算机都是服务器,都是一个处理的节点。
电驴,P2P,区块链,去中心化永远是一个人发展的方向。我们的 C/S 架构,以后就会发生变化。
1.4.1.1 Managed Beans (MBeans)
An MBean is a Java object that implements a specific interface and conforms to certain design patterns. These requirements formalize the representation of the resource’s management interface in the MBean. The management interface of a resource is the set of all necessary information and controls that a management application needs to operate on the resource. The management interface of an MBean is represented as: ■ Valued attributes that can be accessed ■ Operations that can be invoked ■ Notifications that can be emitted (see “Notification Model” on page 29) ■ The constructors for the MBean’s Java class
类:字段方法,属性名
java.lang.Class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootJmxApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootJmxApplication.class, args);
}
}
每一行代码就是一个压栈,压什么东西,就是你参数之类的。
java.lang.reflect.Field
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public final
class Field extends AccessibleObject implements Member {
private Class<?> clazz;
private int slot;
// This is guaranteed to be interned by the VM in the 1.4
// reflection implementation
private String name;
private Class<?> type;
private int modifiers;
// Generics and annotations support
private transient String signature;
// generic info repository; lazily initialized
private transient FieldRepository genericInfo;
private byte[] annotations;
// Cached field accessor created without override
private FieldAccessor fieldAccessor;
// Cached field accessor created with override
private FieldAccessor overrideFieldAccessor;
}
这个东西不是放在方法区也不是放在堆或者栈里边,我们有一个经典的异常 OOM 就是你的 META 信息区不够了,就是 JAVA 8 之后的永久代。堆是放你的活动字段。
final 不能继承,编译期在编译器编译报错,运行期做编译检查,在高并发的时候,它有它的不变性。保存在我们的 永久区 ,也叫 META 区中,proformsize
returnType paramterType Constructor 构造器,构造器和方法有点类似。 JMX 里是 有值的属性,方法,事件,构造器。
詹姆斯高斯林,接受采访时,曾说:“抽象类是 JAVA 设计最失败的地方。”
rt.jar (runtime) 谁来加载 rt.jar jar 包,就是 bootstrapClassLoder
BoostrapClassLoader 为什么返回 Null 。是因为,java 不希望你改变它的类,ClassLoader 可以改变一些类,为了防止一些冲突,为了不相互覆盖。Spring 不允许你返回一个内容。
jconsole
JPS 来看进程
P : PID 进程号,
杀进程的时候,直接杀掉就行
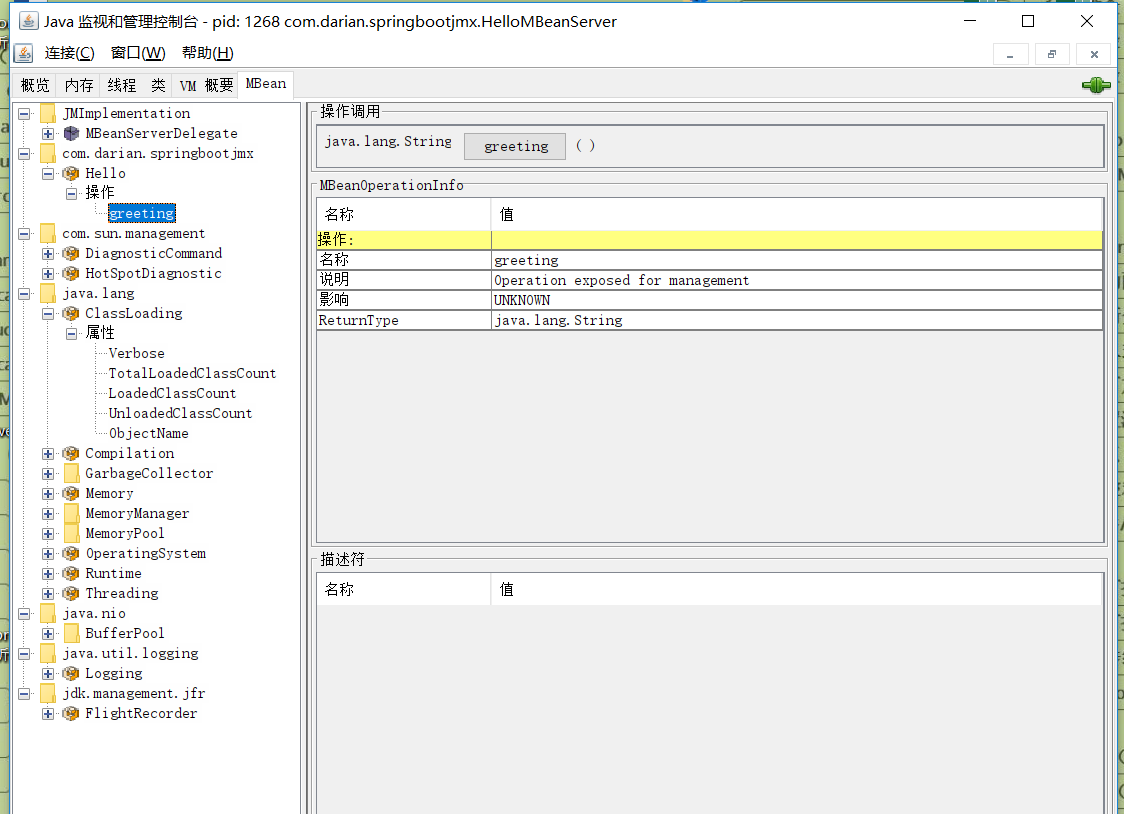
DMBean
你必须是 HelloMBean 实现必须不带 MBean
如果你线上的程序出现了问题。你要去做一些 dump ,这样子就可以去做,你的线上缓存出现问题了,你要清缓存怎么办?你是留 HTTP 接口呢?你就需要写一个 Spring MVC 的类,那么你的这个代码需要自己去写。
我如果实现一个标准的 MBean 的方式,那么我就可以通过 JAVA 内部的相应的操作,告诉你,那些是通过 JAVA 管理的方式来进行托管。比如说你要加开关啊,清缓存啊。监控一下数据啊。
JMS 不需要特定的客户端,如果你的程序不是 Web 程序也可以做。你设置成 jar 报的时候,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class Hello implements HelloMBean {
private String value;
@Override
public String greeting() {
return "Hello, World。";
}
@Override
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String getValue() {
return this.value;
}
}
java 管理拓展,
管理,就是后门。
Security 安全,这个方法是否调用是安全的问题。
Java VisualVM
- 右
- reafactor
- Extract
- Interface
- Extract
- reafactor
Integration
4.1. Exporting Your Beans to JMX
如果你来做,怎么做 Refrence
4.1.1. Creating an MBeanServer
你学习 spring, spring boot 的时候,大家要了解 JAVA 东西。
Spring 、 Spring Boot ** 是 **二流 的技术。大家平时不用的是 一流 的技术。因为这种设计远比 Spring Boot 复杂很多。考虑很多,网络环境,JDK 的兼容,等等等等诸如此类的问题,Spring Boot 基于 JAVA 做的。
看源码要明白它背后的实现逻辑。
org.springframework.jmx.support.MBeanServerFactoryBean#getObject
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws MBeanServerNotFoundException {
// .....
// Create a new MBeanServer and register it, if desired.
if (this.server == null) {
this.server = createMBeanServer(this.defaultDomain, this.registerWithFactory);
this.newlyRegistered = this.registerWithFactory;
}
}
protected MBeanServer createMBeanServer(@Nullable String defaultDomain, boolean registerWithFactory) {
if (registerWithFactory) {
return MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer(defaultDomain);
}
else {
return MBeanServerFactory.newMBeanServer(defaultDomain);
}
}
其实Spring Boot 只是对 JAVA 的封装,JAVA 的底层其实是非常琐碎的。Spring Boot 提供了一种新型的方式来做。
面试题怎么解?我们的面试官和候选人都存在问题。面试官不知道面试题背后的由来,面试者知其然不知其所以然,所以就会两个瞎子,容易产生冲突。你了解底层的时候,回答起来就可能不一样了,在战术上边要尊重他,在战略上面要藐视它,你要感觉他不懂,你就将你的就好了。他也不可能也面面俱到。
老外曾说,中国没有高级程序员,可能急于求成的原因。立志成为一个高级程序员。一个没底气,一个偏颇。
spring boot 1.4.7
Monitoring and management over JMX
Java Management Extensions (JMX) provide a standard mechanism to monitor and manage applications. By default Spring Boot will create an MBeanServer with bean id ‘mbeanServer’ and expose any of your beans that are annotated with Spring JMX annotations (
@ManagedResource,@ManagedAttribute,@ManagedOperation). See theJmxAutoConfigurationclass for more details.
org.springframework.jmx.export.SpringModelMBean
1
2
3
public class SpringModelMBean extends RequiredModelMBean {
// 把 ClassLoader 换了一下,包装了一下。
private ClassLoader managedResourceClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
javax.management.modelmbean.RequiredModelMBean 一流
org.springframework.jmx.export.SpringModelMBean二流
javax.management.modelmbean.RequiredModelMBean#load
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public void load()
throws MBeanException, RuntimeOperationsException,
InstanceNotFoundException {
final ServiceNotFoundException x = new ServiceNotFoundException(
"Persistence not supported for this MBean");
throw new MBeanException(x, x.getMessage());
}
他并没有实现,简化了很多操作。
把它的代码敲一遍,比较他们的不同。
不要记 API ,聪明人记方法。负载因子,还有 初始大小 ,JDK 6 和 JDK 8 不一样。记住他完全没有意义。你要记住 API 所代表的 意义 。
API 记不住也没关系。JAVA 标准不会变,假如你有天不用 Spring 了,可能就变了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
@Component
@ManagedResource
public class Person {
private String name;
private String discription;
@ManagedAttribute(defaultValue = "Darian1996 will go",
description = "这是一个名称字段!")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDiscription() {
return discription;
}
public void setDiscription(String discription) {
this.discription = discription;
}
}
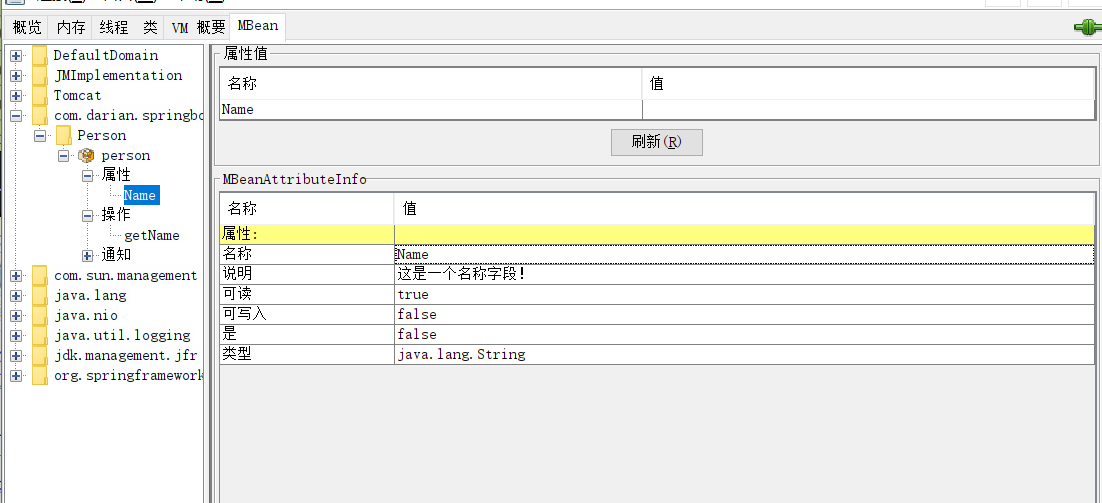
javax.management.MBeanAttributeInfo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
/**
* @serial The actual attribute type.
*/
private final String attributeType;
/**
* @serial The attribute write right.
*/
private final boolean isWrite;
/**
* @serial The attribute read right.
*/
private final boolean isRead;
/**
* @serial Indicates if this method is a "is"
*/
private final boolean is;
/**
* Constructs an {@code MBeanAttributeInfo} object.
*
* @param name The name of the attribute.
* @param type The type or class name of the attribute.
* @param description A human readable description of the attribute.
* @param isReadable True if the attribute has a getter method, false otherwise.
* @param isWritable True if the attribute has a setter method, false otherwise.
* @param isIs True if this attribute has an "is" getter, false otherwise.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code isIs} is true but
* {@code isReadable} is not, or if {@code isIs} is true and
* {@code type} is not {@code boolean} or {@code java.lang.Boolean}.
* (New code should always use {@code boolean} rather than
* {@code java.lang.Boolean}.)
*/
public MBeanAttributeInfo(String name,
String type,
String description,
boolean isReadable,
boolean isWritable,
boolean isIs) {
this(name, type, description, isReadable, isWritable, isIs,
(Descriptor) null);
}
- info 是只读
- Action 是一个操作写 (操作完,没有返回值)
- Action_info 就是一个既读既写 。 (操作完还要返回值)
QA
-
jconsole 如何在 Linux 下做监控?
JPS
jstack
jmap
-
JMX
答:为了生产而准备,为了做嵌入式
-
JMX 可视化:
55.3 Using Jolokia for JMX over HTTP
Jolokia is a JMX-HTTP bridge that provides an alternative method of accessing JMX beans. To use Jolokia, include a dependency to
org.jolokia:jolokia-core. For example, with Maven, you would add the following dependency:1 2 3 4
<dependency> <groupId>org.jolokia</groupId> <artifactId>jolokia-core</artifactId> </dependency>
通过 http 暴漏
-
http 1.x 不如 RPC
-
Spring Boot 要看看的 它的源代码。
-
好的面试官,知道你的学习方法对就行了,
-
jconsole 集成了 jvisualVM 的一些功能。