议题
- 设计基石
- 结构模式
- 模式差异
- 课堂小结
- 问答互动
设计基石
- 封装
- 对象之间联系
- 继承
- 对象之间层次
- 多态
- 对象之间差异
对象之间的联系,调用,
父类,子类,继承
结构模式
- 代理模式
- 适配器模式
- 装饰器模式
- 享元模式
- 组合模式
- 门面模式
- 桥接模式
适配器模式
- 特点:将一个接口转换成为客户端的一个接口
- 关系:适配接口和被适配接口没有层次关系
- 距离:
Java AWT、Java I/O、Spring Web MVC
java.awt.event.MouseListener 是观察者的变种。
java.awt.event.MouseAdapter
1
public abstract class MouseAdapter implements MouseListener, MouseWheelListener, MouseMotionListener {
- 适配器可以有多实现,有滑轮,又有拖放
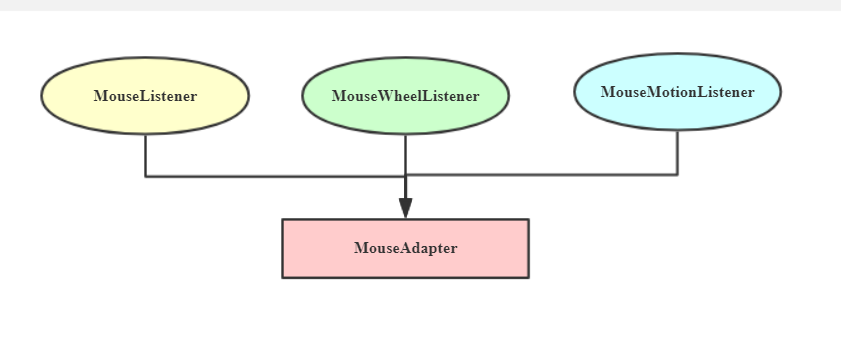
适配器:
字节流转化成为字符流,通过 Adapter 进行转化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class FileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException, FileNotFoundException {
// 目前拥有的实例
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("aaa");
// 需要的对象
// InputStream -> Reader
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "UTF-8");
print(reader);
}
private static void print(Reader reader){
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@RestController
public class OopDesignPatternApplication extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@GetMapping("")
public String hello(){
return "hello, world";
}
}
装饰器模式
- 特点:动态的添加或者覆盖被包装者的接口行为
- 关系:装饰者和被装饰者有层次关系
- 举例:
Spring I/O、Spring Core、Spring Web MVC
org.springframework.core.DecoratingClassLoader 就是继承加上多态。
享元模式
- 特点:共享对象状态,减少重复创建
- 关系:享元对象缓存共享实体
- 举例:
Integer 缓存、String intern、Thread Local
这个对象是经常用到的。
Integer
String
ThreadLocal * ThreadlocalMap
享元模式和单例模式有异曲同工模式,
单例:双检查锁。
容器缓存也是,JVM 也是。
主要是 复用
组合模式
- 特点:执行组合对象时如同执行其元素对象
- 关系:组合对象和被组合对象是相同类型
- 举例:
EL、Spring Cache、Spring Web MVC
很重要,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public class CompositeDemo {
private static interface A{
void save();
}
private static class AImpl implements A{
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("save();");
}
}
/**
* 可实现可不实现
**/
private static class CompositeA implements A{
private Collection<A> list = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void save() {
list.forEach(a -> a.save());
}
}
}
逐一的去处理,迭代的去处理。(组合模式)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public Object getValue(ELContext context, Object base, Object property) {
context.setPropertyResolved(false);
int sz = this.size;
for(int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
Object result = this.resolvers[i].getValue(context, base, property);
if (context.isPropertyResolved()) {
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
org.springframework.cache.support.CompositeCacheManager
代理一般是一对一的关系
缓存,一层一层的缓存,只关心存储这件事情。
组合模式:
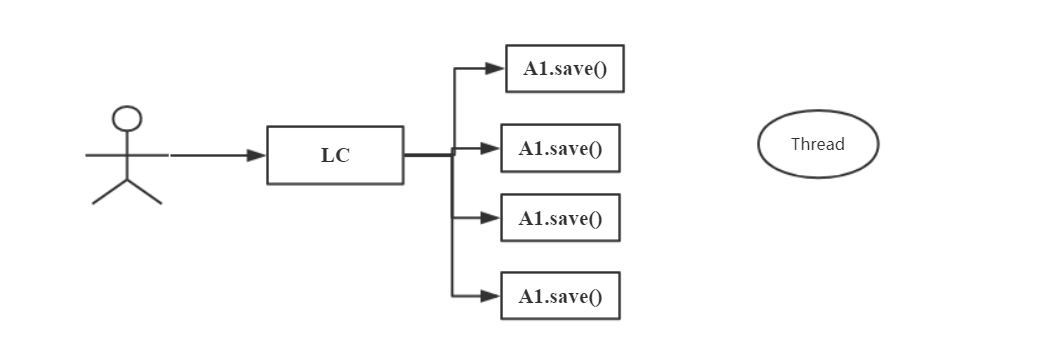
代理模式:
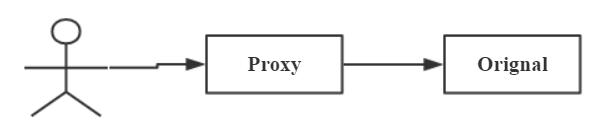
一般来说,
发消息,有可能是一对一,有可能是一对多。
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerComposite
1
2
3
4
class WebMvcConfigurerComposite implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final List<WebMvcConfigurer> delegates = new ArrayList();
// ...
}
如果是相同类型,我感受不到是组合还是不是组合。
门面模式
- 特点:简化接口,聚合子系统实现
- 关系:门面接口和子系统接口自由组合实现
- 举例:Tomcat
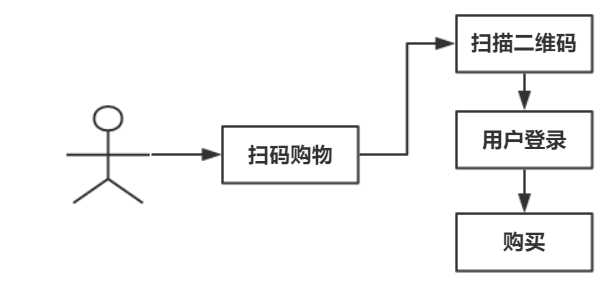
面向对象接口编程比较琐碎。A、B、C 数据属于相对独立的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class FacadeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
private static class ServiceA{
private void save(){
}
}
private static class ServiceB{
private void save(){
}
}
private static class ServiceFacade{
private ServiceA serviceA;
private ServiceB serviceB;
private void service(){
serviceA.save();
serviceB.save();
}
}
}
总计
享元模式一对多,与业务没有太多的关系。
组合模式。多个元素组合执行
门面模式。多个子系统组合执行
接口爆炸,
缺点:
入参会比较复杂,调用链路越长,入参越多,越复杂,用户体验好,但是实现起来不好实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
private boolean detectAllHandlerMappings = true;
private boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters = true;
private boolean detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers = true;
private boolean detectAllViewResolvers = true;
private boolean throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound = false;
private boolean cleanupAfterInclude = true;
@Nullable
private MultipartResolver multipartResolver;
@Nullable
private LocaleResolver localeResolver;
@Nullable
private ThemeResolver themeResolver;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerExceptionResolver> handlerExceptionResolvers;
@Nullable
private RequestToViewNameTranslator viewNameTranslator;
@Nullable
private FlashMapManager flashMapManager;
@Nullable
private List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
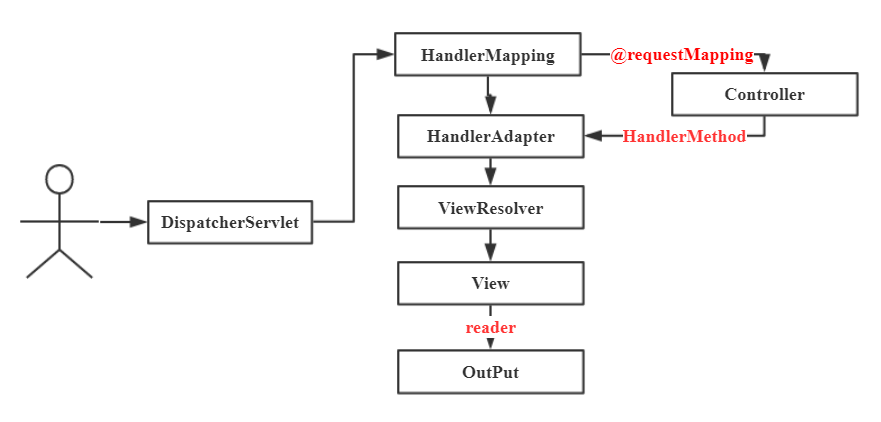
HandlerMapping 就是组合模式,
桥接模式
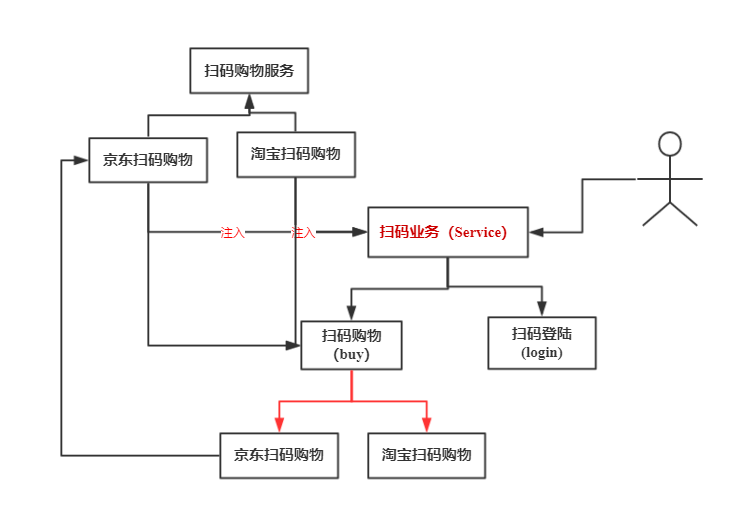
JDBC里边
Preparement
同时注入是策略模式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
public class BirdgeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScanService scanService = new scanServiceImpl(new ScanbuyService() {
@Override
public void buy() {
System.out.println("JD 扫码购物");
}
}, null);
// scanService.scanBuy() -> scanBuyService.buy();
// 对于客户端而言,只关注与粗粒度接口,具体执行方法是由运行时初始化而定。
scanService.scanbuy();
scanService = new scanServiceImpl(new ScanbuyService() {
@Override
public void buy() {
System.out.println("TaoBao 扫码购物");
}
}, null);
}
static class scanServiceImpl implements ScanService {
private ScanbuyService scanbuyService;
private ScanLoginService scanLoginService;
scanServiceImpl(ScanbuyService scanbuyService, ScanLoginService scanLoginService) {
this.scanbuyService = scanbuyService;
this.scanLoginService = scanLoginService;
}
@Override
public void scanbuy() {
scanbuyService.buy();
}
@Override
public void scanLogin() {
scanLoginService.login();
}
}
interface ScanService {
void scanbuy();
void scanLogin();
}
interface ScanbuyService {
void buy();
}
interface ScanLoginService {
void login();
}
}
设计模式重要的是思想,
我调用你的时候,我才注入。