JAVA 8 异步并发编程
Java 9 发布了。
oracle 要和 Java 分手。
###
议题
- Java 1.4 时代
- Java 5 时代
- Java 7 时代
- Java 8 时代
Java 5 前时代
- 并发实现
- Java Green Thread
- Java Native Thread
- 编程模型
- Thread
- Runnable
Green thread
现在一般都是 6 以上的了
Green Thread : 绿色线程,它是在 JDK 1.1, 1.2 的时候,由于 Java linux 内核限制。线程和进程没有区别的。所以没有办法启动线程。线程和进程的区别。
进程开销比较大。进程间的上下文切换,线程里边也是有的。在 Linux 中,线程就是微进程! 协程, GO 里边,比线程更小,开销更小。
Green threads
In computer programming, green threads are threads that are scheduled by a runtime library or virtual machine (VM) instead of natively by the underlying operating system. Green threads emulate multithreaded environments without relying on any native OS capabilities, and they are managed in user space instead of kernel space, enabling them to work in environments that do not have native thread support.[1]
- Green threads significantly outperform Linux native threads on thread activation and synchronization.
- Linux native threads have slightly better performance on I/O and context switching operations.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class ThreadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 子线程
new Thread(() ->
System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]hello\n", Thread.currentThread().getName()), "sub"
).start();
System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]start......\n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
1
2
[Thread: main ]start......
[Thread: sub ]hello
Runable 是不一定可以执行完毕的,他和操作系统的调度有关系。
指令重排序
重排序,AMD和Inter是不一样的。
重排序和 CPU 架构是有关系的。
Inter 32 位机器是没有重排的, Inter 64 和 AMD 才有的。
JAVA 的多线程之所以简单,是因为,
线程是有所谓的优先级和父子关系。
实现局限性
- 缺少线程管理的原生支持
- 缺少执行完成的原生支持
- 执行结果获取困难
- 缺少“锁” API
- Double Check Locking 不确定性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
/****
* synchronized 关键字是一种编程语言修饰符号
*/
@Override
public synchronized void run() {
System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]hello\n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}, "sub");
Java 5 会有 Lock 的支持。
拿到线程的运行完成
如果你想要在 线程外边加一个字段 finished 作为 线程的执行状态,内置类只能通过构造器的方式传进去,或者说你用 AtomicBoolean 是 JAVA 5 的东西。
假如说,我们想要去做,怎么办?
实现 Runnable 接口,要把状态传递出去,就需要有一个 #getConpleted 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class CompletedRunableMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CompletedRunable completedRunable = new CompletedRunable();
Thread thread = new Thread(completedRunable, "sub");
thread.start();
// 等这个线程去死,就是串行操作了。带 synchronized 关键字
thread.join();
System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]start......\n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.printf("runable is completed: %s \n",
completedRunable.isCompleted());
}
private static class CompletedRunable implements Runnable {
private volatile boolean completed = false;
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]hello\n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
completed = true;
}
public boolean isCompleted() {
return completed;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
[Thread: sub ]hello
[Thread: main ]start......
runable is completed: true
//-----如果没有 join() ---- : runable is completed: false
如果没有 join() —- : runable is completed: false ,
加上 volatile 也不行。
1
private volatile boolean completed = false;
必须用 #join() 方法。
它会强制等它执行完毕,它就会变成 串行操作了。嵌套线程的情况下,需要 synchronized 关键字
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/**
* Waits for this thread to die.
*/
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
join(0);
}
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
//。。。。。。
}
Java 5
- 并发框架
J.U.C=java.util.concurrent
- 编程模型
ExecutorRunnable、CallableFuture
ExecutorService Demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class ExecutorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 执行器,线程池(ThreadProolExecutor)是它的一种实现
Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
executor.execute(() -> System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]hello.....\n", Thread.currentThread().getName()));
// 合理的关闭线程池是非常重要的
if(executor instanceof ExecutorService){
ExecutorService executorService = ExecutorService.class.cast(executor);
executorService.shutdown();
}
// Java 5 开始实施 AutoCloseable, I/O , JDBC
// 自动关闭
}
}
下边的写法就行:
1
2
3
4
5
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
executorService.execute(() -> System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]hello.....\n", Thread.currentThread().getName()));
executorService.shutdown();
}
Java 5 开始实施 AutoCloseable
- I/O
- JDBC
为什么 ExecutorService 没有实现?
Callable Demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
/**
* <br>Callable是有返回值的操作,相当于Runable
* <br>Darian
**/
public class CalllableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//执行器服务,线程池(ThreadPoolExecutor)是它的一种实现
// 线程池是线程的复用。
ExecutorService executorService =
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(() -> "[Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] : hello,world");
// join 挂了,get()没挂
// Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then retrieves its result.
// 等待它知道成功。
String value = future.get();
System.out.println(value);
// finally
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
1
[Thread: pool-1-thread-1] : hello,world
大家应该思考为什么新的 API 会出来?
Future 的前身是 #join() ,线程池是线程的复用。
比如说,你在 Future 执行的时候,底层错误,或者有运行异常的时候,都会抛出来。
一般都是 try catch finnal 做这件事情
Future Demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class FutureDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//执行器服务,线程池(ThreadPoolExecutor)是它的一种实现
// 线程池是线程的复用。
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(() -> "[Thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] : hello,world");
// 等待完成
while (true){
// 知道当前的操作是否完成
if(future.isDone()){
break;
}
}
// future#get()方法会阻塞当前的线程
String value = future.get();
System.out.println(value);
// finally
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
while (true) .......... 也是阻塞。 #get() 也是阻塞。
抛出的 J.U.C 的 InterruptedException 异常的方法都是阻塞的。
Future 我可以知道我当前的线程是否完成。
单例模式的 DCL Double Check Locking
Java 7
- 并行框架
ForkJoin
- 编程模型
ForkJoinPoolForkJoinTaskRecursiveAction
Fork 是把叉子, Join 是一个 push 你去完成的方式。
Fork 大概就是 递归的二分法的方式。
FockJoin 代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
/**
* <br>
* Fork/Join计算
* 递归的二分法
* 并行计算
* <br>Darian
**/
public class Fork_Join {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 并行:多核心参与
// 并发:一同参与
// JorkJoinPool 线程池:ForkJoinPool
System.out.printf("当前 公用ForkJoin线程池 并行数:%d\n", ForkJoinPool.commonPool().getParallelism());
System.out.printf("当前CPU 处理器数:%d\n", Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
// 与 ThreadPoolExecutor 类似
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
// invoke 调用的意思
forkJoinPool.invoke(new RecursiveAction() {
@Override
protected void compute() {
System.out.printf("[Thread: %s ]: hello。。。。\n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
forkJoinPool.shutdown();
}
}
1
2
3
当前 公用ForkJoin线程池 并行数:11
当前CPU 处理器数:12
[Thread: ForkJoinPool-1-worker-19 ]: hello。。。。
FockJoin 就是 Future 的一个扩展。
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool#invoke 最后也是调用的 #join 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
public <T> T invoke(ForkJoinTask<T> task) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
externalSubmit(task);
return task.join();
}
并行计算
- 并行:多核心参与
- 并发:一块参与
- FockJoin 线程池 : FockJoinPool
写一个并行计算求和的 JAVA 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
/**
* <br>
* 1-10累加
* <br>Darian
**/
public class ForkJoinDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
List<Integer> nums = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
// 累加对象,Java 8 中
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
// RecursiveAction 递归操作
Addtask addtask = new Addtask(nums, longAdder);
forkJoinPool.invoke(addtask);
forkJoinPool.shutdown();
System.out.println(nums + "累加的结果:" + longAdder);
}
private static class Addtask extends RecursiveAction {
private final List<Integer> nums;
private final LongAdder longAdder;
public Addtask(List<Integer> nums, LongAdder longAdder) {
this.nums = nums;
this.longAdder = longAdder;
}
@Override
protected void compute() {
int size = nums.size();
if (size > 1) {
// 二分法
int parts = size / 2;
// 上半部
List<Integer> leftPart = nums.subList(0, parts);
Addtask leftTask = new Addtask(leftPart, longAdder);
// 下半部
List<Integer> rightPart = nums.subList(parts, size);
Addtask rightTask = new Addtask(rightPart, longAdder);
invokeAll(leftTask, rightTask); // fork/join 操作
} else {// 当前的元素只有一个
if (size == 0) {// 保护
return;
}
Integer value = nums.get(0);
// 累加
longAdder.add(value.longValue());
}
}
}
}
LongAddrJAVA 8 的一个累加对象,把任何丢进去,一分为二。递归再递归- 分成左任务,右任务
- 累加进去。
- 分成左任务,右任务
一个数也好,一百万个数也好,丢进去,首先进行 join 的一个操作。
累加的图解:
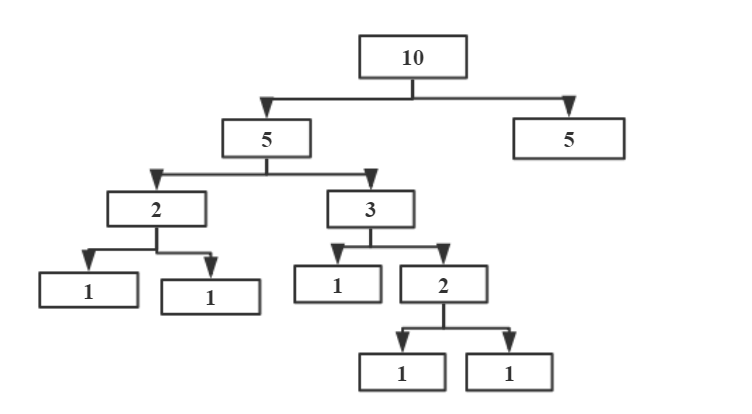
memery reduce 也是聚合。
Future 的限制
- 无法手动完成
- 阻塞式结果返回
- 无法链式多个Future
- 无法合并多个Future结果
- 缺少异常处理
无法合并多个 Future 结果
java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService#invokeAll(java.util.Collection<? extends java.util.concurrent.Callable<T>>)
这是一个一列 Future ,你不得不一个一个一个的做,每一个
#get都是阻塞,所以就变成同步了。并行变成串行了。
缺少异常处理:
当线程里边抛出一个异常
当一个线程内报错误的时候,可能导致也该线程挂掉。没有办法处理异常。只能够看着他,出现异常可能会导致线程池里边的一个线程挂掉。(有可能把它吞了)
没有办法处理异常的。
架构师的好与不好,在于如何把一个场景说清楚,每种技术衍生出来并不是无中生有,一定是遇到了很多问题。不断地衍进,你只有了解它的场景的时候,你才会合理的使用工具类也好,框架也好,才会更加的合理。
不是 学个 JAVA 8 、JAVA 9 就行了。
Java 8 时代
- 异步并行框架
- Fork/Join
- 编程模型
CompletionStageCompletableFuture
CompletionStage
函数式编程的问题:
Supplier<T>
#get方法,提供者,提供方,是一个给予数据的。
Function<T, R>
#apply这是一个函数式操作,操作,操作的返回值。利用函数的值,返回一个什么样的值。
它有 同步 还有 异步
#apply
#supplier
com.darian.java8concurrency.Java8.CompletableFutureDemo1 同步
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class CompletableFutureDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/**
* 1. 完成操作(可以被其他线程去做)
**/
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<String>();
completableFuture.complete("Hello, World");
String value = completableFuture.get();
System.out.println(value);
}
}
就像一个 #get, #set 的方法,我们 complete 方法可以放到其它线程里边去做。
Future 只有 #get #cancle 方法,没有完成的操作!!!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
public boolean complete(T value) {
boolean triggered = completeValue(value);
postComplete();
return triggered;
}
}
final boolean completeValue(T t) {
return RESULT.compareAndSet(this, null, (t == null) ? NIL : t);
}
final void postComplete() {
/*
* On each step, variable f holds current dependents to pop
* and run. It is extended along only one path at a time,
* pushing others to avoid unbounded recursion.
*/
CompletableFuture<?> f = this; Completion h;
while ((h = f.stack) != null ||
(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {
CompletableFuture<?> d; Completion t;
if (STACK.compareAndSet(f, h, t = h.next)) {
if (t != null) {
if (f != this) {
pushStack(h);
continue;
}
NEXT.compareAndSet(h, t, null); // try to detach
}
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;
}
}
/** Traverses stack and unlinks one or more dead Completions, if found. */
final void cleanStack() {
Completion p = stack;
// ensure head of stack live
for (boolean unlinked = false;;) {
if (p == null)
return;
else if (p.isLive()) {
if (unlinked)
return;
else
break;
}
else if (STACK.weakCompareAndSet(this, p, (p = p.next)))
unlinked = true;
else
p = stack;
}
// try to unlink first non-live
for (Completion q = p.next; q != null;) {
Completion s = q.next;
if (q.isLive()) {
p = q;
q = s;
} else if (NEXT.weakCompareAndSet(p, q, s))
break;
else
q = p.next;
}
}
}
get 的时候也是,这种 result
当你更新成功的时候,就是成功,当你更新失败的时候,就失败。
这个状态变更以后,去 #get 的时候,如果状态对直接返回,状态不对的时候,直接就爆出错误了。
com.darian.java8concurrency.Java8.CompletableFutureDemo2 异步阻塞
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class CompletableFutureDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/**
* 2. 异步执行,阻塞操作
**/
CompletableFuture asyncCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("hello, world"));
// 仍然是阻塞操作
asyncCompletableFuture.get();
System.out.println("Starting......");
}
}
如果 需要顺序,仍然需要 #get 去阻塞。
com.darian.java8concurrency.Java8.CompletableFutureDemo3 异步操作,还是阻塞。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class CompletableFutureDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
/**
* 真正的异步
**/
// 非 lambda 写法
CompletableFuture asyncCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
return "hello.World";
}
});
// lambda 写法
CompletableFuture<String> asynoCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 获取数据操作,假设来自于数据库
return String.format("[Thread: %s ]hello。。。。\n",
Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
String value = asynoCompletableFuture.get();
System.out.println("value = " + value);
System.out.println(String.format("[Thread: %s ]starting。。。。\n",
Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
}
1
2
3
value = [Thread: ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-19 ]hello。。。。
[Thread: main ]starting。。。。
com.darian.java8concurrency.Java8.CompletableFutureDemo4 多个操作合并操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
public class CompletableFutureDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 合并操作
**/
// reactive -> flatMap 有点像
CompletableFuture combinedCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 获取数据操作,假设来自于数据库
return String.format("[Thread: %s ]hello。。。。\n",
Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenApply(value -> {
return value + "---来自于数据库" + "[" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]";
}).thenApply(value -> {
// int i = 1 / 0;
return value + " at " + LocalDate.now();
}).thenApply(value -> {
System.out.println(value);
return value;
}).thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("操作结束");
}).exceptionally(CompletableFutureDemo4::apply);
// while (!asynoCompletableFuture.isDone()) {
// }
System.out.println("starting........");
System.in.read();
}
private static Void apply(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println(throwable);
return null;
}
}
1
2
3
4
starting........
[Thread: ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-19 ]hello。。。。
---来自于数据库[ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-19] at 2018-12-23
操作结束
非常像 JS 就像 reactive -> flatMap
需要把值给返回。
当我们使用 Future 的时候,我们用异步的操作的时候,在使用异步的操作,整个放在异步的线程里边,作为一个流水线的操作,
如果 是事务,最后 #commit ,没有结果,是可能强制执行完成。
ForkJoin 是并行提高它的效率
当我们异步异步执行的时候,我们假设,需要某个操作比较费时,会阻塞你的主线程。为了异步操作。提高响应事件。
异步操作: 不强制要求必须返回。
RT response Time 响应时间。
Java 9
GE代替CMS
Spring 5
QPS
TPS
异步操作的特点。不强求及时的返回。
Mono 就是一个 Future
WebFlux
异步操作提高吞吐量
同步操作 5 秒
异步操作 5 秒以上,
吞吐量是要以时间来衡量的。24 小时不间断操作。吞吐量就上去了。
- QPS 100 (每次操作 5 s)
- QPS,10000 (每次操作 50 ms)
因为 没有立马返回,都是在后台一直的计算,但是要执行多久,还是要执行多久。
异步线程没有返回,
Q:异步操作
-
返回结果没有立马给到浏览器,那浏览器什么时候取得响应?
答:和以往的理解不同,不依赖完整的返回内容,比如Json,也有继续等待的方式。
-
Spring 的东西
ListenableFuture<T>可以实现回调。成功回调,失败回到,都有。1 2
public interface ListenableFutureCallback<T> extends SuccessCallback<T>, FailureCallback { }
1 2 3 4
@FunctionalInterface public interface SuccessCallback<T> { void onSuccess(@Nullable T var1); }
1 2 3 4
@FunctionalInterface public interface FailureCallback { void onFailure(Throwable var1); }
org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallbackRegistry1 2 3 4 5 6 7
public class ListenableFutureCallbackRegistry<T> { private final Queue<SuccessCallback<? super T>> successCallbacks = new LinkedList(); private final Queue<FailureCallback> failureCallbacks = new LinkedList(); public void addCallback(ListenableFutureCallback<? super T> callback) { // .......... } }
重点 completableFuture
关注一下
StampedLock- 提供了乐观锁的一种方式
java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap